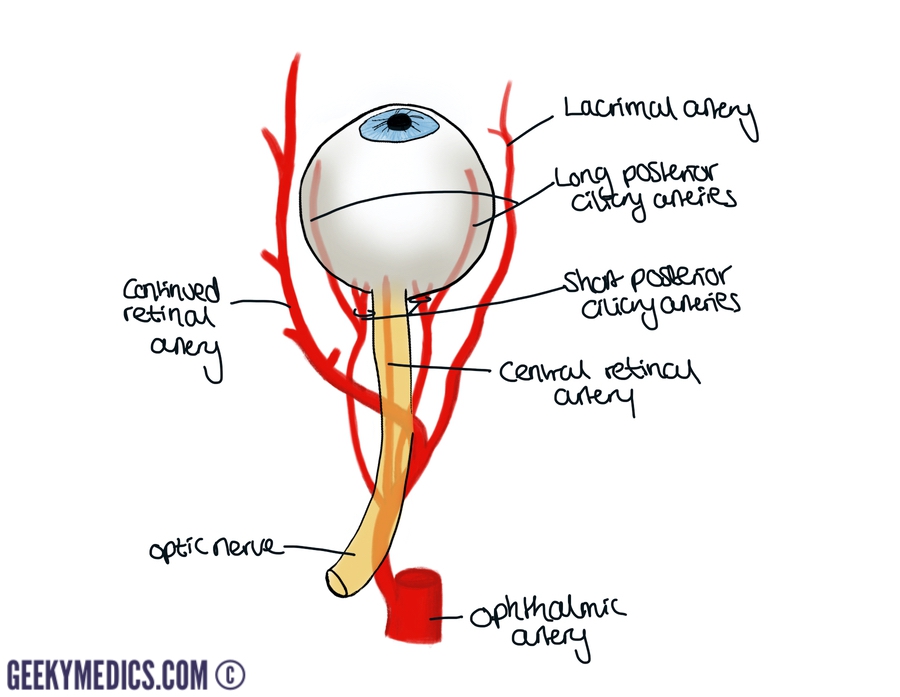
The ophthalmic artery, the first major branch of the internal carotid artery, enters the orbit via the superior orbital fissure, whereupon it gives off the central artery of the retina and branches to the extraocular muscles. It also ascends on the lateral surface of the optic nerve and gives the lacrimal artery. The lacrimal artery has a recurrent meningeal branch that anastomoses with the anterior branch of the middle meningeal artery, creating an anastomosis between the internal and external carotid arteries.
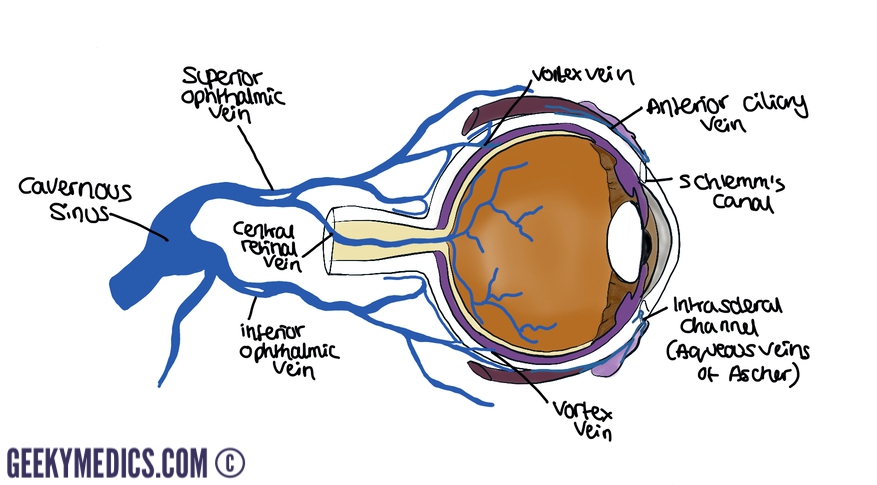
The superior ophthalmic vein leaves the orbit through the superior orbital fissure to enter the cavernous sinus. The inferior ophthalmic vein may join the superior vein, cavernous sinus, or even the pterygoid venous plexus in the infratemporal fossa.
