
The cranium (specifically the neurocranium) is the superoposterior part of the skull that houses and protects the brain. It can be split into the calvarium (skull cap) and cranial base with the remainder of the skull being the facial skeleton. It consists of 8 of the 22 skull bones: the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, temporal (x2), parietal (x2) and occipital bones. Many structures pass into and out of the cranial cavity in the skull via foramina of the skull base.
Bony junctions & landmarks
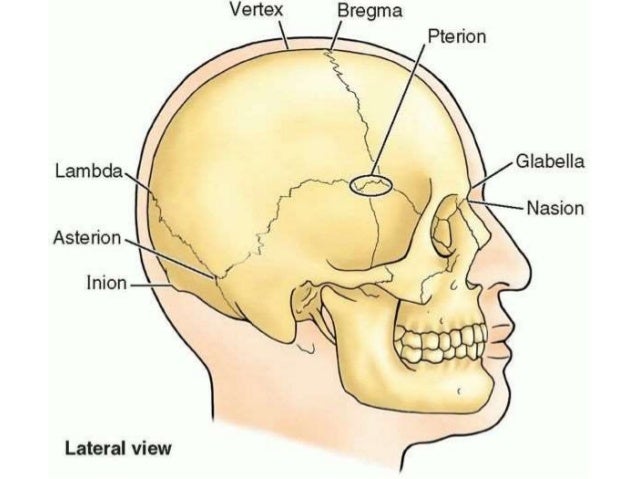
Notable landmarks on the cranium include:
- vertex: most superior point of the skull, midline between the parietal bones.
- inion: highest point of the occipital protuberance (of the occipital bone) at the lower back of the skull.
- areas where numerous skull bones join including:
- Pterion: “H” shaped, between parietal, sphenoid, temporal and frontal bones
- Bregma: between frontal and parietal bones
- Lambda: between occipital and parietal bones
- Asterion: between temporal, occipital and parietal bones
- Nasion: between frontal and nasal bones
CLINICAL CORNER
Due to its thinness, trauma to the pterion can cause epidural haemorrhage from rupture of the anterior branch of the middle meningeal artery underneath.
